
Absolute or dynamic viscosity is used to calculate Reynold's Number to determine if a fluid flow is laminar, transient or turbulent. The unit of viscosity is newton-second per square meter, which is usually expressed as pascal-second in SI units.The viscosity of a fluid is a measure of its resistance to gradual deformation by shear stress or tensile stress.įor further definitions, go to Absolute (dynamic) and kinematic viscosity.
It takes about 0.01 poise, or 0.001 Pa.s, for water to be very viscous at 20☌ (Pascal seconds). The dyne sec/cm2 is used more often and is called “Poise.” One Pa is worth ten Poise. The Pascal second (Pa s) is the SI unit of viscosity, and the Poiseuille is the name for it.
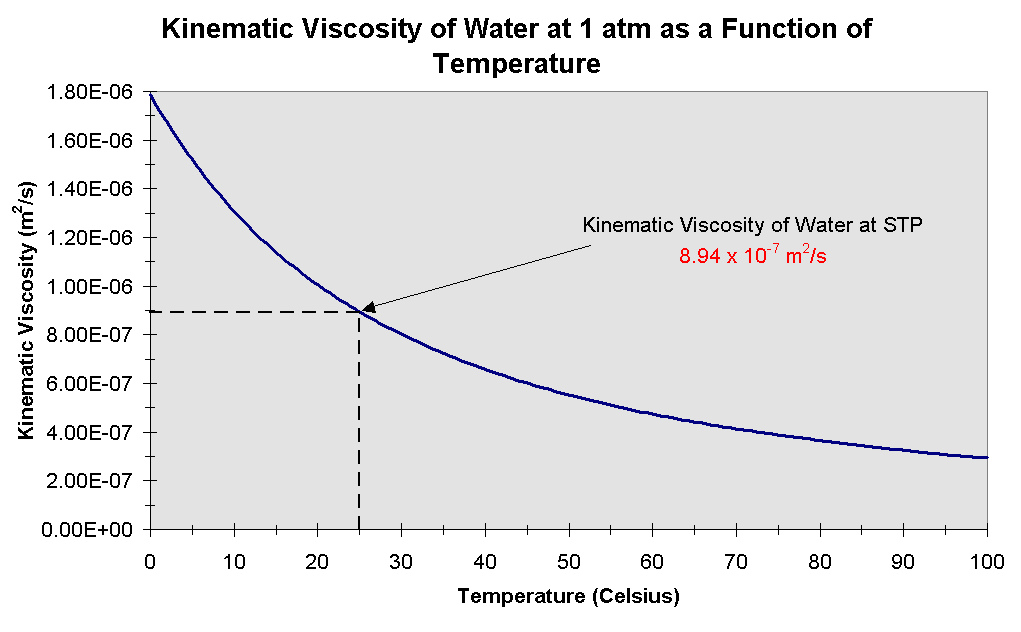
The viscosity of a fluid is used to describe how difficult it is for a fluid to flow and how difficult it is for an object to move through a fluid. The viscosity of water changes with its temperature, and the greater the temperature, the less viscous the water becomes. What is the viscosity of water and what are SI units of viscosity?Īt 20 ☌, water has a viscosity of 1.0016 millipascals per second. In contrast, turbulent flow is a type of fluid in which the fluid fluctuates and mixes irregularly. Laminar flow is a form of fluid (gas or liquid) flow in which the fluid flows smoothly and in predictable patterns. Fluids that have no or minimal internal friction resistance are categorized as non-viscous fluids. The degree of resistance between the fluid layers is measured by viscosity, which is a fluid factor. The force required to rotate the probe or torque is used to estimate viscosity.ĭoes not depends upon the density of a fluid.Ī viscous fluid is defined as a fluid with high flow resistance. These instruments rotate a probe in a liquid sample. The time is converted directly to kinematic viscosity using a calibration constant provided for the specific tube.ĭynamic viscosity is measured using rotational viscometers. The kinematic viscosity of a fluid is measured by determining the time it takes to flow through a capillary tube. Kinematic viscosity is the measure of a fluid’s resistance to flow in the absence of an external force other than gravity.ĭynamic viscosity is a measure of a fluid’s resistance to flow when an external force is applied. The Difference between Kinematic Viscosity and Dynamic Viscosity Kinematic viscosity is a key fuel attribute that determines the atomization quality and size of the fuel droplet in the spray.
Water at 20 ☌ has a kinematic viscosity of about 1 cSt (1mm 2/s).ġ stokes = 100 centistokes = 1 cm 2/sec = 0.0001 m 2/sec. Kinematic viscosity is the internal resistance of a fluid to flow under gravitational forces.

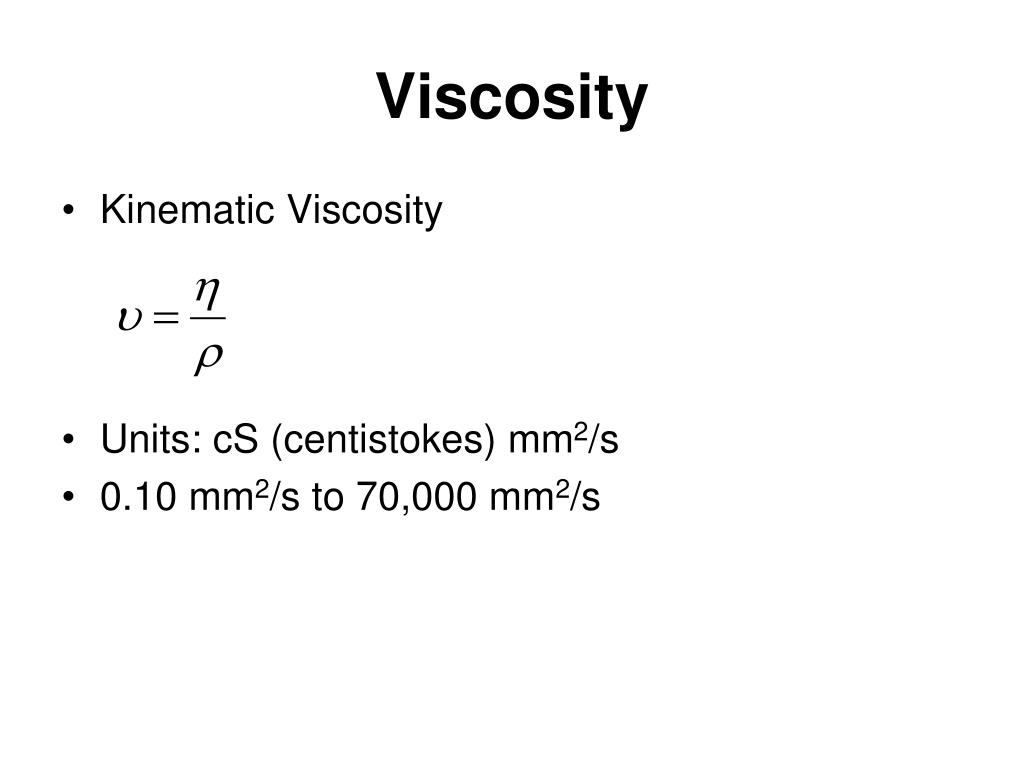
Key Points Definition of kinematic viscosity Viscosity reporting is only valid if the temperature at which the test was performed is also provided, such as 23 cSt at 40 degrees C. This number is translated into scientific quantities such as centistokes (cSt) or square millimeters per second. It is calculated by measuring the duration in seconds necessary for a set volume of fluid to flow a known distance by gravity via a capillary within a calibrated viscometer at a well-regulated temperature. Other units are: 1 St ( Stoke) = 1 cm 2/s = 10 −4 m 2/s. The SI unit of the kinematic viscosity is m 2/s. The kinematic viscosity of a fluid is the ratio of its dynamic viscosity to its density.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
